What Is the Difference Between Income and Net Worth?
12 Min Read | Jun 11, 2024

Do you remember dreaming of a big salary and a corner office as a college kid because you thought a good income would make you rich? But once you hit the “real world,” that corner office probably looked more like a middle-row cubicle. And that big salary was likely missing a zero or two. (Disappointing, we know.)
But after a couple of promotions, you’re now making a lot more money than you used to. (Thank goodness!)
A lot of people use income as the primary measuring stick for financial success. But is it really the best indicator of wealth? What about your net worth? And what’s the difference between the two, anyway?
While your income tells you how much money you bring in every year, your net worth gives you a true picture of where you stand financially. Let’s dive into the differences between income and net worth and find out how those differences might affect your retirement future.
What Is Net Worth?
Net worth is simply what you own (assets) minus what you owe (liabilities). In other words, the total value of your assets minus your liabilities—aka debt—equals your net worth.
For example, if you own a home worth $300,000 and you owe $100,000 on it, you have $200,000 in equity toward your net worth. So to calculate your total net worth, add up the value of all the things you own and subtract how much you owe (if anything) on those things.
What is the average net worth in America?
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the median net worth of American households is $192,084.1 A lot of that wealth comes from retirement accounts (like a 401(k) and IRA) and home equity (or how much of your home you actually own).2 Here’s a breakdown of median net worth by age:
- Under 35: $30,500
- 35–44: $126,900
- 45–54: $186,000
- 55–64: $276,000
- 65–69: $341,400
- 70–74: $373,900
- 75 and up: $315,9003
How do you figure out where your current net worth stacks up? Let’s find out.
How to Determine Your Net Worth
Figuring out your net worth is actually pretty simple. All you have to do is add up all your liabilities and subtract it from the value of your assets (the current value of property you own plus money in your financial accounts—think emergency fund, retirement savings, checking account, etc.).
Here’s what a list of all your assets and liabilities might look like:
|
Assets |
Liabilities |
|
Home value: $300,000 Car worth: $25,000 401(k)/retirement savings: $50,000 Emergency savings: $5,000 Checking account: $2,000 |
Mortgage balance: $100,000 Car loan: $20,000 Credit card debt: $15,000 Student loan debt: $60,000 Medical bills: $1,000 |
|
Total: $382,000 |
Total: $196,000 |
| $382,000 - $196,000 = $186,000 Net Worth | |
Or you could save some time by using our nifty Net Worth Calculator for an easy peasy way to figure out your net worth.
Once you calculate your net worth, you might be surprised to find out how much you have—or don’t have. And yes, it’s possible to have a negative net worth.
But remember, there’s always time to improve your finances and grow your wealth right where you are. So let this number serve as motivation, not shame, to clean up your mess or continue building wealth. And what’s the best tool for building wealth and improving your net worth? Let’s find out.
What Is Income?
In a nutshell, income is money you receive on a regular basis, usually through work or investments.
Find out your net worth with this free calculator!
There are a lot of ways you can earn income: The paycheck you get every two weeks from your job or the profits from the business you own and operate. The dividends or compound growth you earn from the mutual funds you invested in. The cash you made last weekend selling old records or baseball cards at a garage sale. All of that counts as income!
And since we’re on the topic of income, let’s explore the difference between gross income and net income:
- Gross income is the amount of money you make before taxes and other deductions are taken out of your paycheck. For example, if you earn $50,000 a year and get paid monthly, your gross pay is $4,167.
- Net income, on the other hand, is what you actually bring home after taxes and payroll deductions like Social Security and 401(k) contributions. Your monthly net income could look something like this: $4,167 (gross) - $1,200 (taxes and deductions) = $2,967 (net).
Here’s the bottom line: Your income is your biggest wealth-building tool—so use your paycheck and other forms of income to your advantage.
Fun fact: The median household income in America is about $74,580.4 If you invest 15% of that income for 30 years at an 11% annual return, you could have about $2.6 million in your nest egg by the time you retire!
Make an Investment Plan With a Pro
SmartVestor shows you up to five investing professionals in your area for free. No commitments, no hidden fees.
Ramsey Solutions is a paid, non-client promoter of participating pros.
How Is Income Different From Net Worth?
Even though it’s your biggest wealth-building tool, income is only part of your financial picture. Think of it this way: Your income is how you make money, but your net worth measures your actual level of wealth, providing a much more accurate picture of your overall financial health.
So, even if you earn that sweet promotion, complete with a swanky corner office and a hefty pay raise, you can still have a low (or negative) net worth if you’ve got debt holding your head underwater. Check it out.
Is It Better to Have a Higher Income or Higher Net Worth?
Let’s pretend Katie is a marketing executive who makes $150,000 a year and has a net worth of $20,000. Her friend Lacy is a schoolteacher who makes $45,000 a year and has a net worth of $250,000.
Question: Who has more wealth—the marketing executive or the schoolteacher?
You got it. Lacy the schoolteacher actually has more wealth because she has a higher net worth than her friend Katie.
That’s why we say your income isn’t an accurate snapshot of your financial situation. Because when it comes to wealth, it really doesn’t matter how large your income is. Yes, you can build wealth faster with a larger income, but income alone doesn’t make you wealthy. You could make $1 million a year and spend $2 million—meaning you’d be in debt up to your eyeballs.
No, it’s what you do with your income that matters most. Whether you make $500,000 or $50,000 a year, you have to save and invest that income throughout your career if you want to build wealth. And yes—you could earn $50,000 a year (for your entire life) and still retire a millionaire—we see that happen all the time!
Some quick math shows that if you’re debt-free with a $50,000 salary and you invest 15% of your income for 30 years, you could have over $1.7 million saved for retirement. On the other hand, a person making twice that income who never invests even a small portion of it will likely come up short in retirement.
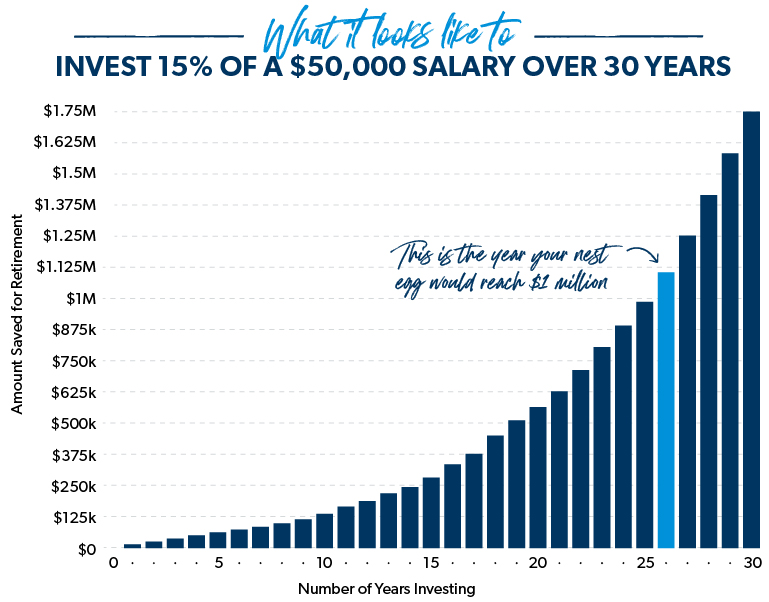
At the end of the day, a large income doesn’t necessarily lead to large net worth—especially if you’re saddled with student loans and car debt and you’re always trying to keep up with the Joneses.
How to Improve Your Net Worth
Your net worth shows you three big things: Where you are now, what needs to be fixed, and how far you need to go.
If you’re ahead of the game—awesome—keep doing what you’re doing and build on the momentum you already have. But if you’re staring at your net worth and not liking what you see, it’s time to get serious. Here’s what to do.
Stop giving away your money.
Katie gets paid on Friday after an exhausting week of work. To blow off steam, she decides to hit the town with her BFFs all weekend. You know, Starbucks, brunch, Starbucks, shopping, Starbucks, dinner and cocktails—the basics.
By Monday morning, Katie’s paycheck is basically gone, maybe leaving a few hundred bucks to cover credit card bills and food. Katie is living paycheck to paycheck. Katie is in debt. Katie is not building wealth.
Remember when we said income is your biggest wealth-building tool? Well, that tool only works when you don’t give it all away.
Give every dollar a name and create a budget. This way, you’ll know exactly where your money goes so you can cut back on unnecessary expenses and spending—like the gym membership you never use, expensive latte orders, or that streaming subscription you forgot to cancel.
Follow the 7 Baby Steps.
The 7 Baby Steps are a proven plan for creating an emergency fund, paying off debt for good, and building wealth—all of which raise your net worth. See what we did there?
So, if you’re finally ready to stop giving your money away and increase your net worth, it’s time to step up to the plate.
Baby Step 1: Save $1,000 as fast as you can for your starter emergency fund. This will help keep you from slipping even further into debt (relying on credit cards or loans) when unexpected life events happen. And just like that, you’ve already started improving your net worth.
Baby Step 2: Pay off all debt (except the house) using the debt snowball. Debt is like that toxic “friend” who keeps dragging you down. You need to cut it out of your life. List all your debts from smallest to largest and use the debt snowball method to attack each balance with a vengeance.
Baby Step 3: Save 3–6 months of expenses in a fully funded emergency fund. Your debt is gone (except the house). Hooray! Now, take all the money you were throwing at debt and use it to build a fully funded emergency fund to protect you and your family from life’s biggest surprises.
By now, you’ve already made huge improvements to your net worth by getting rid of crushing liabilities and bulking up your financial assets (your fully funded emergency savings). But don’t stop now. Keep going!
Baby Step 4: Invest 15% of your household income in retirement. Now we’re cooking! Focus on regularly investing 15% of your gross income in a retirement savings account—like a workplace 401(k). You’ll continue to increase your net worth and you’ll build wealth for your golden years. Nice!
Baby Step 5: Save for your children’s college fund. We recommend 529 college savings plans or ESAs (education savings accounts). Both of these accounts are considered assets for the account owner (usually the parent).
Baby Step 6: Pay off your home early. Paying off your home mortgage is like beating the final boss in Super Mario Bros. This is the big dog, baby. When your home turns from liability to asset, your net worth skyrockets.
Baby Step 7: Build wealth and give. You know what people without debt can do? Whatever they want! Now that you have a net worth you can be proud of, you’re ready to live and give like no one else. But are you a millionaire yet?
When Do You Become a Millionaire?
You’re a millionaire when your net worth—not your income—reaches $1 million. So if you have $700,000 in your savings accounts and retirement accounts, a paid-for home worth $300,000, and no debt whatsoever, congratulations—you’re a millionaire! Go out and celebrate with a nice steak dinner or a beach vacation. You’ve earned it!
You might think millionaire status is out of reach, but you’d be surprised how much the average millionaire looks just like you.
Let’s look at income for example. Only 31% of millionaires had an average annual household income of $100,000 or more over the course of their careers, according to The National Study of Millionaires. In fact, the study found that one-third of millionaires never had a six-figure household income in a single year. Let that sink in for a minute.
And do you want to take a guess which three careers produce the most millionaires in America today? Here they are: engineer, accountant and teacher. The truth is, you don’t need to be a doctor or CEO of some big company in order to reach millionaire status—that’s a myth! Anyone and everyone in America today can become a millionaire.
When we talk to millionaires about their success with money, they don’t mention an inheritance or winning the lottery. They talk about smart saving, wise spending and investing practices, and living without debt.
Dave's new book, Baby Steps Millionaires, will show you the proven path that millions of Americans have taken to become millionaires—and how you can become one too. Grab your copy today to learn how to bust through the barriers preventing you from becoming a millionaire.
Did You Just Get a Net Worth Wake-Up Call?
You’ve learned that income is what you earn from working and net worth is the value of your personal assets minus any debt. Now you should be able to crunch some numbers to determine where you stand financially. Are you making a great salary but have nothing to show for it? Or do you have an average salary and want to change your spending habits so you can invest and save more for retirement?
The good news is, you’re the one in the driver’s seat. You can make the necessary changes to your finances so you can enjoy the retirement of your dreams. Start by talking to a financial advisor or investment professional who can help you create a game plan for investing. If you need help finding a professional near you, check out the SmartVestor program.
Expert Advice Delivered Straight to Your Inbox
Our weekly email newsletter is full of practical advice you can easily apply to your daily routine so you can win with your money, relationships and career.
This article provides general guidelines about investing topics. Your situation may be unique. To discuss a plan for your situation, connect with a SmartVestor Pro. Ramsey Solutions is a paid, non-client promoter of participating Pros.



